Brass Casting and Brass Casting Services: Precision, Durability, and Versatility in Metal Manufacturing
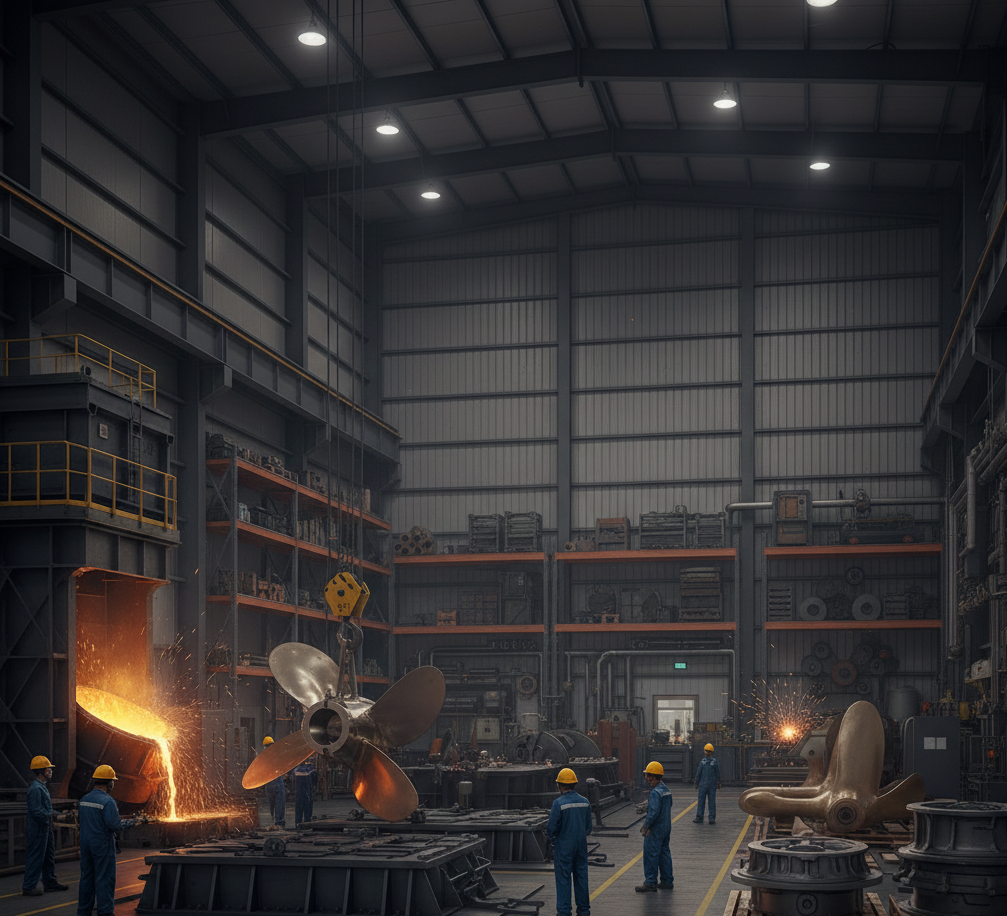

Brass has long been valued for its corrosion resistance, strength, and aesthetic appeal. It is an alloy of copper and zinc that combines durability with excellent machinability and thermal conductivity. Brass casting allows manufacturers to produce complex components with precision, while brass casting services provide the expertise, equipment, and quality assurance necessary for producing high-performance metal parts. These services play a vital role across industries, including plumbing, automotive, electronics, marine, construction, and decorative applications.
Understanding Brass Casting
Brass casting is the process of forming metal components by pouring molten brass into molds to produce parts with specific shapes, sizes, and tolerances. Brass’s unique combination of copper and zinc offers excellent mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and an attractive surface finish, making it ideal for functional and decorative applications.
Casting brass allows manufacturers to produce complex geometries, intricate designs, hollow structures, and fine details that are difficult or expensive to achieve with machining alone. It also enables the production of durable components capable of withstanding wear, heat, and environmental exposure.
Types of Brass Used in Casting
Several brass alloys are suitable for casting, each with distinct properties tailored to specific applications:
-
Alpha Brass
Alpha brass contains less than 35% zinc and offers excellent corrosion resistance and machinability. It is ideal for plumbing fittings, valves, and precision components. -
Alpha-Beta Brass (Duplex Brass)
This alloy contains 35–45% zinc and balances strength with ductility. It is widely used in castings that require higher mechanical strength, such as gears, marine hardware, and industrial fittings. -
Beta Brass
Beta brass contains more than 45% zinc, providing high strength but reduced corrosion resistance. It is used in applications where mechanical durability is prioritized over environmental exposure.
The Brass Casting Process
Brass casting involves several critical steps to ensure high-quality, precise, and reliable components:
1. Pattern Making
Manufacturers create a pattern, a replica of the final component, using wood, metal, or plastic. Patterns include allowances for metal shrinkage and machining. Accurate pattern design ensures the finished component meets dimensional and structural requirements.
2. Mold Preparation
Molds can be made from sand, metal, or ceramic materials, depending on the desired production method. Sand molds are common for their flexibility and ability to accommodate complex geometries. Technicians pack the sand around the pattern to create the mold cavity, which defines the component’s shape.
3. Core Making
Cores are used to create hollow sections or intricate internal cavities. Technicians place cores inside the mold, shaping areas that the molten brass should not fill. Correct core placement is essential for accurate and defect-free castings.
4. Melting and Pouring
Brass is melted in furnaces, typically gas-fired or electric induction furnaces, reaching temperatures around 900–950°C (1650–1750°F). Workers monitor the molten metal carefully to maintain fluidity and prevent oxidation. The molten brass is then poured into the mold cavity, filling every section of the mold.
5. Cooling and Solidification
The molten brass solidifies in the mold. Controlled cooling prevents shrinkage defects, cracks, and internal stresses. Cooling rates depend on mold material, part thickness, and alloy composition.
6. Mold Removal
After solidification, the mold is removed. Sand molds are typically broken, while permanent molds can be opened and reused. The raw casting is then cleaned and prepared for finishing processes.
7. Finishing and Quality Inspection
Finishing processes include grinding, polishing, deburring, machining, and heat treatment to enhance surface quality and meet dimensional tolerances. Rigorous quality inspection, including dimensional verification and non-destructive testing, ensures that each component meets industry standards and client specifications.
Advantages of Brass Casting
Brass casting offers numerous advantages that make it a preferred choice for manufacturers:
-
Corrosion Resistance
Brass naturally resists corrosion from water, air, and many chemicals, making it ideal for plumbing, marine, and outdoor applications. -
Durability and Strength
Brass components withstand mechanical stress, wear, and high temperatures, ensuring longevity and reliable performance. -
Excellent Machinability
Brass is easy to machine, drill, and finish, allowing for high precision and fine detail in components. -
Complex Geometry Capability
Casting enables the creation of intricate designs, internal cavities, and thin walls that are difficult or expensive to achieve with machining. -
Aesthetic Appeal
Brass naturally produces a bright, golden finish that enhances the visual appeal of decorative and architectural components.
Applications of Brass Casting
Brass casting serves a wide range of industries due to its combination of mechanical, chemical, and aesthetic properties:
1. Plumbing and Valves
Brass is widely used in faucets, valves, pipe fittings, and connectors due to its corrosion resistance, durability, and ease of machining. Cast brass components provide long-lasting performance in water systems and plumbing infrastructure.
2. Automotive Industry
Brass casting produces gears, bearings, bushings, and radiator components. Its strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability make it suitable for both functional and structural automotive parts.
3. Marine Applications
Brass is ideal for marine hardware, propellers, and fittings because it withstands exposure to saltwater, corrosion, and harsh environments. Its durability ensures long-term performance in demanding marine conditions.
4. Industrial Machinery
Brass components such as valves, gears, pumps, and electrical connectors are widely used in industrial machinery due to their wear resistance, precision, and thermal conductivity.
5. Decorative and Architectural Elements
Brass casting enables designers and architects to create ornamental railings, gates, furniture, lighting fixtures, and decorative sculptures. The alloy’s natural color and polishability enhance the visual appeal of finished products.
6. Electrical and Electronics
Brass’s conductivity and corrosion resistance make it suitable for connectors, terminals, switch components, and other electrical hardware where reliability and performance are critical.
Selecting Brass Casting Services
Choosing the right brass casting service provider ensures high-quality, durable components. Consider the following factors:
-
Experience and Expertise
Providers should have a proven track record in casting various brass alloys and producing components for multiple industries. -
Advanced Technology
Facilities with automated pouring, CNC machining, and inspection equipment ensure consistent quality and precision. -
Customization Capabilities
The service should accommodate prototypes, small batch production, and high-volume orders while allowing design flexibility. -
Quality Assurance
Rigorous quality control, including dimensional verification, metallurgical testing, and non-destructive testing, guarantees components meet industry standards. -
Timely Delivery
Reliable production schedules and project management ensure components are delivered on time without compromising quality.
Challenges in Brass Casting
Even though brass casting is versatile, it presents certain challenges:
-
Porosity: Gas entrapment during pouring can create cavities. Proper venting and degassing techniques reduce this risk.
-
Shrinkage: Brass contracts as it cools. Accurate pattern design and allowances help manage shrinkage.
-
Oxidation: Molten brass reacts with air. Fluxes and controlled environments minimize surface oxidation and defects.
-
Surface Finish Issues: Complex geometries may require additional polishing or machining to achieve a smooth finish.
Experienced brass casting services apply advanced techniques and quality control to overcome these challenges.
Future Trends in Brass Casting
The brass casting industry continues to evolve with technological advancements:
-
Automation and Robotics: Automated pouring, mold handling, and finishing reduce human error and improve production consistency.
-
3D-Printed Patterns and Molds: Additive manufacturing enables rapid prototyping and complex mold designs.
-
Sustainability: Recycling brass scrap, reducing energy consumption, and using environmentally friendly binders promote sustainable production.
-
Advanced Brass Alloys: Development of specialized brass alloys expands applications in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and decorative industries.
These trends increase efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the quality and reliability of brass components.
Conclusion
Brass casting and brass casting services provide manufacturers with reliable, precise, and durable solutions for a wide range of industries. From plumbing and automotive to marine, industrial machinery, electrical components, and decorative applications, brass castings combine strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal.
Professional brass casting services ensure precision, repeatability, and quality through advanced technology, experienced craftsmanship, and rigorous inspection processes. Innovations in automation, additive manufacturing, and sustainable practices further enhance production efficiency and component performance.
Whether producing a single prototype or thousands of high-precision components, brass casting services deliver cost-effective, reliable, and versatile solutions that meet the demands of modern manufacturing.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness