Food Intolerance & Malabsorption Syndromes
Food plays a central role in our daily lives, but for many people, certain foods can quietly cause discomfort, digestive distress, and long-term health issues. Food intolerance and malabsorption syndromes are common yet often misunderstood conditions that affect how the body processes and absorbs nutrients. Lactose intolerance is one of the most well-known examples, but it is only part of a broader group of digestive disorders. Understanding these conditions is the first step toward effective management and better gut health.
What Is Food Intolerance?
Food intolerance occurs when the digestive system has difficulty breaking down specific foods. Unlike food allergies, which involve the immune system and can be life-threatening, food intolerance is usually related to enzyme deficiencies or sensitivity to certain food components. Symptoms tend to develop gradually and may vary depending on the amount of food consumed. Common intolerances include lactose, gluten (non-celiac sensitivity), fructose, and certain food additives, all of which can disrupt digestive comfort.
Understanding Malabsorption Syndromes
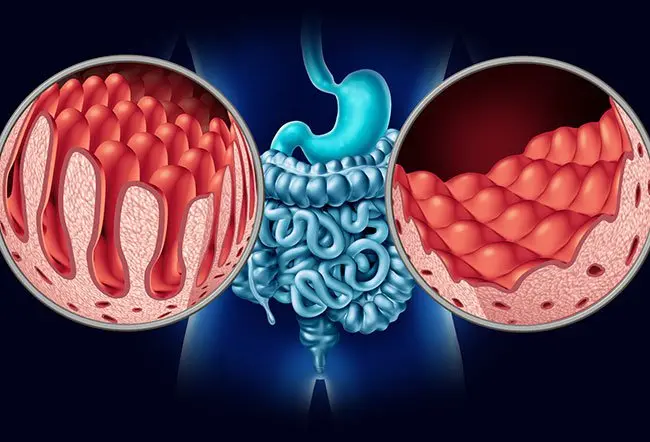
Malabsorption syndromes refer to conditions where the intestines are unable to properly absorb nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. This problem can result from damage to the intestinal lining, enzyme deficiencies, or underlying gastrointestinal diseases. When nutrients are not absorbed efficiently, the body may experience deficiencies that affect energy levels, immunity, bone health, and overall wellbeing. Over time, untreated malabsorption can lead to significant nutritional and health complications.
Lactose Intolerance: The Most Common Example
Lactose intolerance is a classic and widespread form of food intolerance. It occurs when the body lacks sufficient lactase, the enzyme responsible for digesting lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products. Undigested lactose travels to the colon, where it ferments and causes symptoms like bloating, gas, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Lactose intolerance can develop at any age and is more common in adults, particularly in Asian, African, and Middle Eastern populations.
Common Causes of Food Intolerance and Malabsorption
Several factors can contribute to food intolerance and malabsorption syndromes. Genetic enzyme deficiencies, such as lactase deficiency, are a primary cause. Gastrointestinal infections, celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and chronic conditions like pancreatitis can also interfere with digestion and absorption. Additionally, certain medications, surgeries involving the intestines, and prolonged gut inflammation may damage the intestinal lining, reducing its ability to absorb nutrients efficiently.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
The symptoms of food intolerance and malabsorption syndromes can range from mild to severe and often overlap with other digestive disorders. Common signs include bloating, excessive gas, diarrhea, constipation, stomach cramps, nausea, and fatigue. In malabsorption syndromes, additional symptoms such as unexplained weight loss, anemia, brittle nails, hair thinning, and vitamin deficiencies may appear. Because symptoms can be vague, many people remain undiagnosed for years.
How These Conditions Are Diagnosed
Diagnosing food intolerance and malabsorption syndromes requires a combination of medical history, symptom tracking, and diagnostic tests. Breath tests are commonly used to detect lactose and fructose intolerance. Blood tests can identify nutrient deficiencies or conditions like celiac disease. Stool tests may help assess fat malabsorption, while endoscopy or imaging studies can evaluate intestinal health. A gastroenterologist plays a key role in identifying the root cause and guiding appropriate treatment.
Treatment and Management Strategies
Managing food intolerance and malabsorption syndromes focuses on symptom relief, nutritional balance, and addressing underlying causes. Dietary modifications are often the first step, such as reducing or eliminating trigger foods. Enzyme supplements, like lactase tablets, can help some individuals tolerate problematic foods. In malabsorption cases, treating the underlying condition and supplementing deficient nutrients is essential. Long-term success depends on personalized dietary planning and regular medical follow-up.
Lifestyle and Dietary Adjustments for Better Gut Health
Simple lifestyle changes can significantly improve digestive health for individuals with food intolerance or malabsorption issues. Eating smaller, balanced meals, keeping a food diary, staying hydrated, and managing stress can reduce symptoms. Choosing lactose-free dairy alternatives, gluten-free grains when necessary, and nutrient-dense foods helps maintain proper nutrition. Consulting a healthcare professional ensures dietary changes are safe, sustainable, and tailored to individual needs.
Book Appointment with Best Gastroenterologist in Islamabad via InstaCare
If you are experiencing ongoing digestive discomfort, bloating, or unexplained nutritional deficiencies, professional guidance is crucial. A qualified gastroenterologist can accurately diagnose food intolerance or malabsorption syndromes and create a personalized treatment plan. Book an appointment with the best gastroenterologist in Islamabad via InstaCare to receive expert consultation, advanced diagnostic support, and trusted care—all from the convenience of a reliable digital healthcare platform.
Conclusion
Food intolerance and malabsorption syndromes can significantly impact quality of life if left unmanaged. Conditions like lactose intolerance may seem minor at first but can lead to chronic discomfort and nutritional imbalances over time. Early diagnosis, informed dietary choices, and professional medical support are key to managing symptoms effectively. With the right approach and expert care, individuals can regain digestive comfort and enjoy a healthier, more balanced life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between food intolerance and food allergy?
Food intolerance affects digestion and does not involve the immune system, while food allergies trigger an immune response and can be life-threatening even in small amounts.
2. Can lactose intolerance develop later in life?
Yes, lactose intolerance commonly develops in adulthood as lactase enzyme production naturally decreases with age.
3. Are malabsorption syndromes serious?
They can be serious if untreated, as prolonged nutrient deficiencies may lead to anemia, bone loss, fatigue, and weakened immunity.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jogos
- Gardening
- Health
- Início
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Outro
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness